We want you to be in the best possible physical condition for your treatment
Since your diagnosis you may have many questions. These could include:
“What should I be eating?”
“What foods could help my treatment?”
“Are there any foods I should be avoiding?”
Nutrition has a real impact on your bodies ability to manage health.
The most important message is to continue to eat well. Choosing a wide variety of foods and well-balanced meals can help you feel better and optimise your energy levels. Trying to lose weight is generally not encouraged.
What you eat is so important in ensuring you have the best nutrition. Maintaining a good general body condition and weight will enable better outcomes from treatment.
Eating well
‘Eating well’ means choosing a wide variety of foods, which provide enough nutrients to maintain a good nutritional status and maintain your weight. Eating well will also help you to keep up your strength and energy levels, support your immune system, and improve your general well-being.
These nutrients include energy (calories), protein, carbohydrates, fats and vitamins and minerals. Fibre is also important in the diet, as it helps with bowel function, regulates bowel movements and prevents constipation. However, some people may be advised to avoid fibre, particularly those with bowel cancer, ask your dietitian or nurse if you are unsure.
The Eatwell Guide
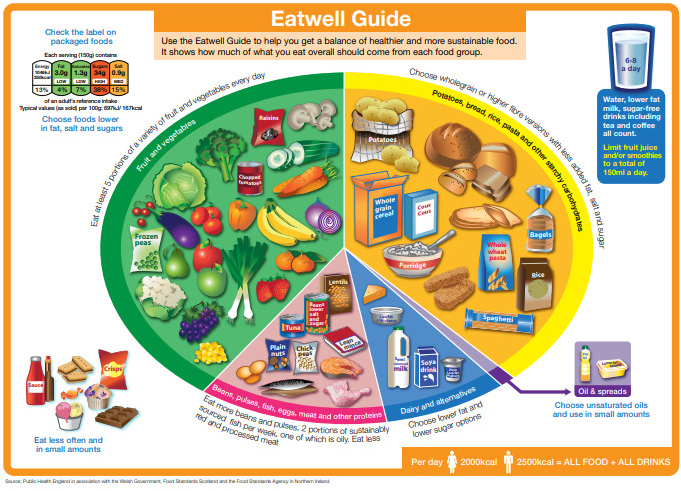
The Eatwell Guide shows the different types of foods and drinks we should consume and the proportions needed to have a healthy, balanced diet. This guide shows the main food groups that form a healthy, balanced diet:
- Eat at least 5 portions of a variety of fruit and vegetables every day. Fresh, frozen, and canned fruits count, but limit dried fruit and fruit juice to just one portion per day. Fruit and vegetables are great for vitamins , minerals and fibre
- Base meals on potatoes, bread, rice, pasta or other starchy carbohydrates; choosing wholegrain versions where possible. These are great for slow-release energy
- Aim for 2 -3 portions of dairy or dairy alternatives (such as soya drinks)per day; choosing lower fat and lower sugar options. Dairy is important for protein and some vitamins such as calcium
- Aim to have regular source of beans, pulses, fish, eggs, meat and other proteins (including 2 portions of fish every week, one of which should be oily). Keep red and processed meats to a minimum . Protein is important for our muscles and bones and protein rich foods also provide vitamins, minerals and essential fatty acids.
- Choose unsaturated oils and spreads and eat in small amounts. Small amount of unsaturated fats provide essential fatty acids and some vitamins
- Drink 6-8 cups/glasses of fluid a day
- Aim to keep foods and drinks high in fat, salt or sugar to a minimum, unless you are trying to boost calories
Make sure you have the right portion sizes of these foods. This information sheet has some examples of portion sizes.
Eating problems and cancer
You may have difficulty eating for a variety of reasons which may include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Constipation
- Swallowing difficulties
- Poor appetite
If you are having difficulty eating, let your doctor or nurse know, as they may be able to help with symptoms or refer you to your local dietitian.
It is important to prevent weight loss if you are having difficulty with eating, and you can do this by boosting calories and protein in your diet.
Calorie Boosting Information
It can be helpful to add extra protein calories in your everyday food to help you to prevent unnecessary weight loss, or may help to put weight on if you need to.
Click on the tabs below to get helpful information on how to increase your calories.
